With proper care, many varieties of flowers can stay fresh for more than a week, and even short-lived ones can be kept fresh for several days. Keeping flowers away from heat is an important way to preserve their freshness. It’s also a good idea to use sugar and acid to energize the flowers, keep the vase clean, and use bleach or other fungicides to get rid of bacteria and fungi.
Cutting and Preparing Flowers
Cut flowers at the correct stage of growth. Different flowers bloom at different times, so they need to be cut at different stages of growth. Flowers with multiple skeletal stems, such as delphiniums and lilacs, should be cut when one skeletal flower is open and the inner color is visible. If there is only one bud on each stem, such as marigolds and sunflowers, cut them after the flowers are fully opened.
Cut when temperatures are low. Flowers lose less water when temperatures are low, so be sure to cut them during the lowest temperatures of the day. Cutting early in the morning is a good choice as less water is lost and the flowers stay fresh longer. You can cut it in the evening, but the flowers will not be nourished by night dew.
Arrange the flowers in a large, clean vase. It must be clean to avoid infection by bacteria and other microorganisms. Choose a container with a neck that is wide enough to accommodate the stems of the flowers.
- Flowers with stems of different lengths should be placed in different vases so that each flower is visible.
Treat freshly cut flowers with hot water (optional). After cutting the flowers, immediately insert their stems into hot water of about 44 degrees Celsius, and then place the vase in a cool place for 1-2 hours. Hot water molecules travel up the stems more easily, and the flowers lose less water in the cooler air. Under the dual action of hot water and cold air, the flowers absorb more moisture, thereby extending the shelf life.
Place the flowers in warm water. The base of the flower’s rhizome should be kept in water. Warm water is easier for flowers to absorb. If you did not perform the previous “fortification” step, you should add water close to room temperature to the vase.
- Flowers with bulbs do well in cold water.
Keep It Fresh
Remove underwater leaves. Leaves underwater can rot and contain bacteria that can infect the entire flower. Whenever you see leaves underwater, remove them.
Change the water. Change the water daily to keep the flowers fresh. Make sure there is no residue in the vase before adding fresh water to reduce the chance of bacterial infection.
- Even if there is fixed foam under the flower branches, it still needs to be soaked with water. Let the bubbles sink naturally without pressing down, otherwise the bubbles will become trapped in the valve stem.
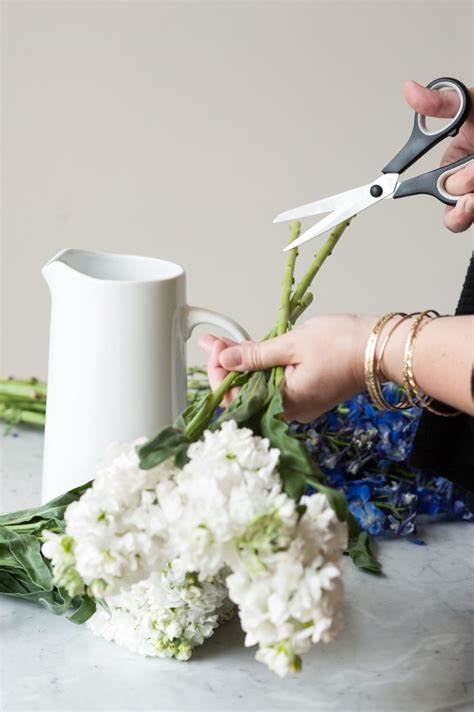
Prune stems regularly. Prune every time you change the water, and at least every few days. Use scissors or a knife to cut a 45-degree bevel. This increases the contact area between the stem and water, allowing it to absorb more water.
- Prune the flower branches bought in the store immediately and put them in the water.
Roses can easily trap air bubbles in their stems, preventing water absorption. Therefore it is best to cut rose branches underwater.
Use flower preservatives. Flower preservatives are available in florists, gardening shops, and supermarkets. Preservatives contain all the nutrients needed for flowers to grow: sugar for energy, acid to protect color and maintain the pH of water, and fungicides to kill bacteria and fungi.
- If you don’t want to buy preservatives, or the preservatives you buy don’t work, you can refer to the following section to make your preservatives.
Stay away from harmful environments. Flowers need to be kept away from direct sunlight and other heat sources such as heaters or the top of the television. Don’t put them in the same room as fruits, as the ethylene released by fruits can cause flowers to wilt. Heating, gentle breezes, and even cold winds can accelerate moisture loss and shorten the shelf life of flowers.
Remove wilted flowers. Whenever you see a wilted flower, remove it or the ethylene it releases will cause a chain reaction that affects other flowers. Use the flower clippings as fertilizer, make dried flowers, or throw them in a trash can in another room.
Homemade Flower Preservative
Add orange soda and bleach to the water. Sprite, 7-up, or other clear soda provides sugar and acid to the flowers, keeping them fresh. The ratio of soda water to pure water is 1:3, and then add a few drops of bleach to kill harmful microorganisms. This mixture works better than many commercial preservatives.
- Don’t use diet soda, the sugar is necessary to provide energy for the flowers.
Do not use strong soda water such as cola, as too much acidity will be harmful to the flowers.
Or use lemon juice, sugar, and bleach to make a preservative. Add 30 ml of lemon juice to 1 liter of water. Add another 1 tablespoon (15 ml) sugar for energy. Like the recipe above, use a few drops of bleach to remove bacteria and fungi.
- If used in a small vase, all you need is a few drops of lemon juice and a few pinches of sugar.
- If the water is hard and contains minerals, you can use more lemon juice to neutralize it. Be careful though, too much acid can be harmful to your flowers.
- The stems of daisies, sunflowers, and other plants in the Asteraceae family secrete a gelatinous substance. If you place these flowers with other flowers, you must add acid to prevent the gum from blocking other flower branches.
Learn about the power of vodka. A few drops of vodka can reduce your flowers’ production of ethylene (the gas that causes them to wilt). Vodka is useful, but it is not a substitute for bleach or other fungicides to destroy microorganisms.
Do not use too much bleaching powder. Bleach is used as a preservative, sometimes more than a few drops per vase. This is dangerous because preservatives are not stable and excessive use can cause flowers and stems to fade.
Be careful with aspirin and vinegar. Grated aspirin and white vinegar can replace acid, but are not as effective as lemon juice and soda. If you take too much aspirin, it will hasten the wilting of the flowers or turn the stems gray.
Understand why copper is useless. Copper can kill fungi, but the copper in copper coins and copper-plated coins is not soluble in water. Throwing a copper coin in the water will not extend the shelf life of the flowers.
Tips
- If a rose is drooping, soak the entire branch in warm water to rehydrate it, but this first aid may not always work.
- Cut daffodils and hyacinths emit a chemical that is harmful to other flowers planted together. So the flowers should be stored separately for at least 12 hours after cutting.
- Removing rose thorns will shorten the life of the rose, but rose thorns can be removed underwater.
- Hairspray is used to style dried flowers, not to preserve them fresh.