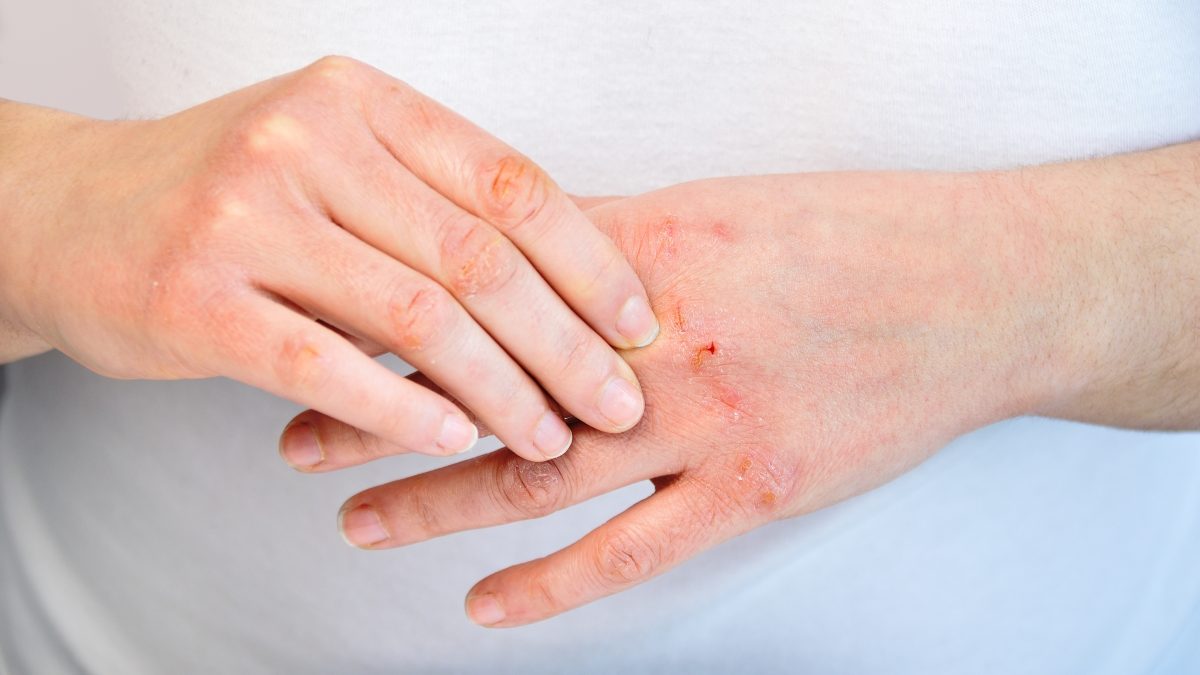
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by inflamed, itchy, and red skin that may flare up periodically. While the exact cause of atopic dermatitis is unknown, genetics and environmental factors are believed to play a role in its development.
In this article, we will discuss the common symptoms of atopic dermatitis and ways to manage them.
The Unbearable Itching
One of the most common and persistent symptoms of atopic dermatitis is intense itching. Itchiness can occur at any time, but it tends to be worse at night. This can be extremely discomforting and may interfere with sleep and daily activities. Scratching the affected areas can provide temporary relief, but can also aggravate the skin and lead to further inflammation.
Dehydrated and Flaky Skin
People with atopic dermatitis often have dry and scaly skin. This is due to the skin’s inability to retain moisture, which leads to excessive dryness. The affected areas may also become crusty, flaky, and thickened over time. This can be a source of embarrassment and self-consciousness for individuals with atopic dermatitis, especially if the affected areas are visible.
Red and Swollen Skin
The skin of someone with atopic dermatitis will typically be red and inflamed. This is caused by an overactive immune response in the body, which triggers inflammation. The affected areas may also be warm to the touch and may appear swollen.
In severe cases, blisters and oozing may also be present.
Rashes
Rashes are a common symptom of atopic dermatitis and can appear anywhere on the body. These rashes may be flat, raised, or have a rough texture. They may also ooze or be covered in crusts. In infants, rashes may appear on the face and scalp, while in older children and adults, rashes tend to appear on the hands, feet, wrists, ankles, and the folds of the arms and legs.
Flare-ups
Atopic dermatitis is characterized by periods of flare-ups and remission. Flare-ups occur when the skin becomes more inflamed and irritated, leading to a worsening of symptoms. These flare-ups can have triggers such as stress, allergens, and irritants like harsh chemicals and fabrics. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Management of Treatments
While there is no cure for atopic dermatitis, there are various ways to manage its symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. The treatment plan will vary depending on the severity of the condition, the age of the patient, and individual needs.
Some common treatments include:
- Topical corticosteroids: These are anti-inflammatory creams or ointments that can help reduce redness and itching.
- Moisturizers: Regularly applying a thick, fragrance-free moisturizer can help keep the skin hydrated and prevent flare-ups.
- Antihistamines: These can help reduce itchiness and improve sleep for those with severe itching.
- Phototherapy: Exposure to controlled amounts of natural or artificial light can help improve symptoms in some cases.
In addition to these treatments, it is essential to develop a good skincare routine and avoid triggers that may worsen symptoms. Keeping the skin clean, avoiding harsh soaps and chemicals, and wearing loose, comfortable clothing can also help manage atopic dermatitis.
Conclusion
Atopic dermatitis symptoms can be uncomfortable and disruptive, but they can be managed with proper care and treatment. If you or a loved one is experiencing these symptoms, it is essential to consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. With the right approach, it is possible to live a comfortable and fulfilling life with atopic dermatitis.